In the electronic world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are often regarded as the "brains" of electronic devices, and the materials used in PCB manufacturing serve as the foundation of this "brain." Different materials endow PCBs with diverse performance characteristics to meet the requirements of various complex application scenarios. In industrial control (IC) PCBs, the material demands are particularly stringent. Let's dive deep into the common materials used in PCBs.
► Organic Resin-Based Materials
1. Phenolic Resin Boards
Phenolic resin boards, known as the "budget-friendly option" among PCB materials, use phenolic resin as the base material. These boards offer moderate mechanical strength and good electrical insulation, meeting the basic requirements of simpler circuits. However, their heat resistance is relatively limited, with a working temperature below 100°C. They are often used in low-performance applications such as vintage radios and children's toys.
2. Epoxy Resin Boards
Epoxy resin boards are among the most widely used PCB materials. With excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, they have secured a solid foothold in the electronics industry. The FR-4 epoxy resin board is the most common, utilized in products ranging from everyday computers and communication devices to consumer electronics.
For high-temperature applications like IC PCBs, high Tg (glass transition temperature) epoxy boards are preferred. These boards exhibit superior thermal resistance, making them ideal for automotive electronics, aerospace equipment, and other high-end fields requiring stable operation under extreme temperatures.
3. Polyimide Boards
Polyimide boards are renowned for their exceptional thermal resistance, boasting a glass transition temperature typically exceeding 200°C and reaching up to 300°C in high-performance variants. Beyond thermal stability, they offer outstanding electrical insulation, mechanical robustness, and chemical resistance.
Thanks to these properties, polyimide boards find application in aerospace, military, and high-speed communication fields. In IC PCBs, polyimide boards are indispensable for high-performance systems operating under extreme conditions, such as core circuit boards in industrial automation control systems.
► Inorganic Material-Based Boards
1. Ceramic Substrates
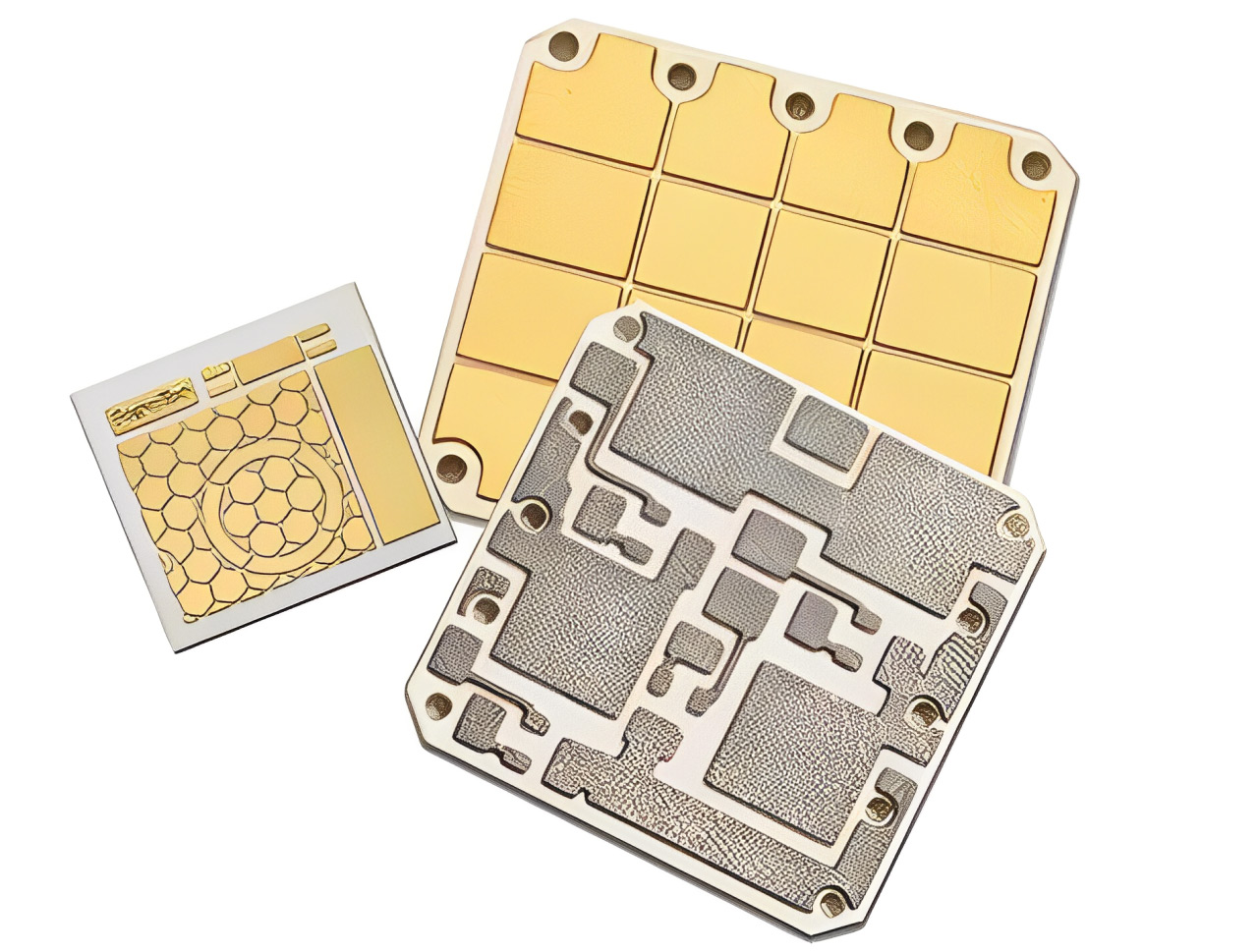
Ceramic substrates leverage ceramic materials as the framework, offering high thermal conductivity, excellent insulation, and superior thermal and chemical resistance. Common ceramic materials include alumina (Al₂O₃) and aluminum nitride (AlN).
Alumina ceramic substrates are widely used in power electronics and thick-film integrated circuits due to their balanced performance. Meanwhile, aluminum nitride substrates, with their exceptional thermal conductivity of 170–230 W/(m·K), approach copper's conductivity levels, making them ideal for high-heat-dissipation applications like high-power LED lighting and RF amplifier modules. In IC PCBs, ceramic substrates effectively address heat dissipation challenges, ensuring long-term operational stability.
2. Metal Core PCBs
Metal core PCBs, including aluminum and copper substrates, excel in thermal management by dissipating heat efficiently.
Aluminum PCBs: Cost-effective and widely applied in the lighting industry, including LED streetlights and indoor illumination systems.
Copper PCBs: With superior thermal conductivity, copper PCBs are more expensive and used in high-demand applications, such as power modules and automotive electronics.
In IC PCBs, metal substrates ensure effective heat dissipation for high-power equipment, safeguarding stable operation.
► Composite Materials
1. Rigid-Flex PCBs
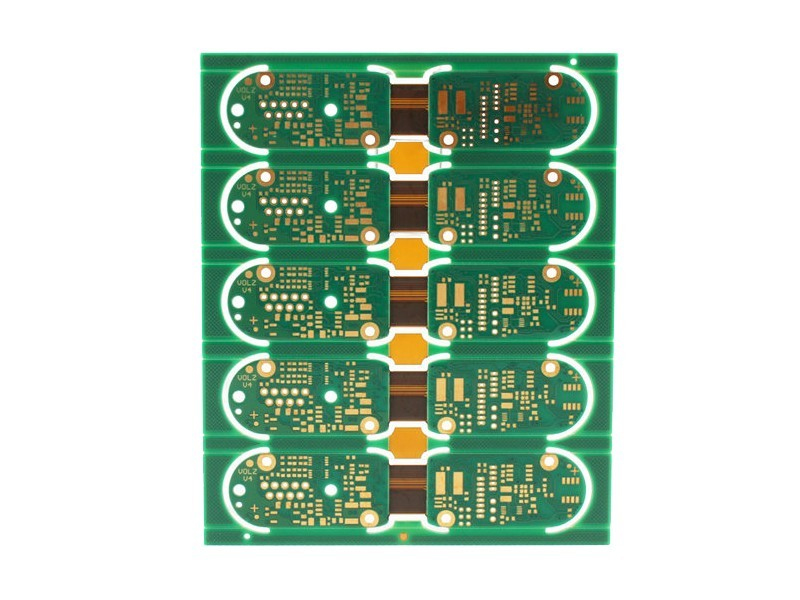
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the structural support of rigid boards with the flexibility of flexible circuits, making them ideal for space-constrained and dynamic bending applications, such as laptop screen connectors and smartphone camera modules. In IC PCBs, rigid-flex boards address intricate wiring and unique installation requirements, reducing size and weight while enhancing integration and reliability—key to miniaturized and high-performance industrial automation devices.
2. Embedded Component PCBs
Embedded component PCBs integrate passive components (resistors, capacitors, inductors) directly into the board, achieving component and PCB unification.
This design significantly reduces PCB size and weight while boosting circuit integration, minimizing electromagnetic interference, and enhancing signal stability. Widely applied in high-end devices like smartphones, tablets, and high-performance servers, embedded component PCBs also play a critical role in IC PCBs by improving industrial control equipment's performance and reliability.