With the continuous development of LED technology, LED lighting devices have become mainstream in the lighting industry due to their energy-saving, long lifespan, and high efficiency. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a crucial role as the core carrier in LED lighting equipment, providing electrical conductivity, heat dissipation, and mechanical support. This article will provide a detailed overview of the applications of PCBs in LED lighting devices and discuss their design requirements.
► PCB Applications in LED Lighting Equipment
In LED lighting systems, PCBs serve as the mechanical support and electrical connection for the LED chips. By mounting the LED chips onto the PCB surface and using conductive layers, the PCB delivers electrical power to the LED components, enabling them to emit light.
-LED Lamps: In common LED lighting fixtures such as ceiling lights, downlights, spotlights, and tube lights, the PCB is the key component that supports and connects the LED chips. These PCBs typically need to possess excellent thermal conductivity and electrical performance to ensure optimal functionality.
LED Displays: Each pixel in an LED display consists of small LED components, which PCBs arrange in a compact configuration to form a high-resolution display system. The PCB for LED displays not only needs to support high-density component placement but also ensure stable performance, preventing issues like flickering, color fading, and light decay.
-LED Backlighting: PCBs are widely used in LED backlighting systems for devices such as mobile phones, televisions, and computer monitors. The PCB provides a stable power supply and conductive paths for LED light strips while helping to evenly distribute light across the display.
► Types of PCBs for LED Lighting Equipment
The choice of PCB type depends on the specific requirements of the LED lighting device. Common types of PCBs used in LED lighting applications include:
-Aluminum-based PCBs are among the most common types used in LED lighting devices. They use aluminum as the substrate material, offering excellent thermal conductivity. The typical structure of an aluminum PCB consists of three layers: the conductive layer, the insulating layer, and the metal base. Aluminum PCBs are commonly used for high-power LED applications such as street lighting and automotive lighting.
-FR-4 PCBs: FR-4 is a glass fiber-reinforced epoxy resin material with good electrical properties and mechanical strength. Although FR-4 PCBs have lower thermal conductivity compared to aluminum-based boards, their lower cost makes them suitable for low-power LED lighting applications.
-Ceramic PCBs: Ceramic-based PCBs are primarily used in high-end LED applications, particularly those operating in high-temperature environments, such as automotive and industrial lighting. Ceramic materials offer excellent thermal dissipation and electrical insulation properties.
► Design Requirements for PCBs in LED Lighting Equipment
When designing PCBs for LED lighting devices, several key factors must be considered to ensure the stability of the LED’s performance and its long operational life.
1. Thermal Management:
One of the major challenges faced by LED lighting systems is heat dissipation. LEDs generate substantial heat during operation, which, if not efficiently dissipated, can lead to light decay, color shift, and even device failure. Therefore, effective thermal management in the PCB design is critical.
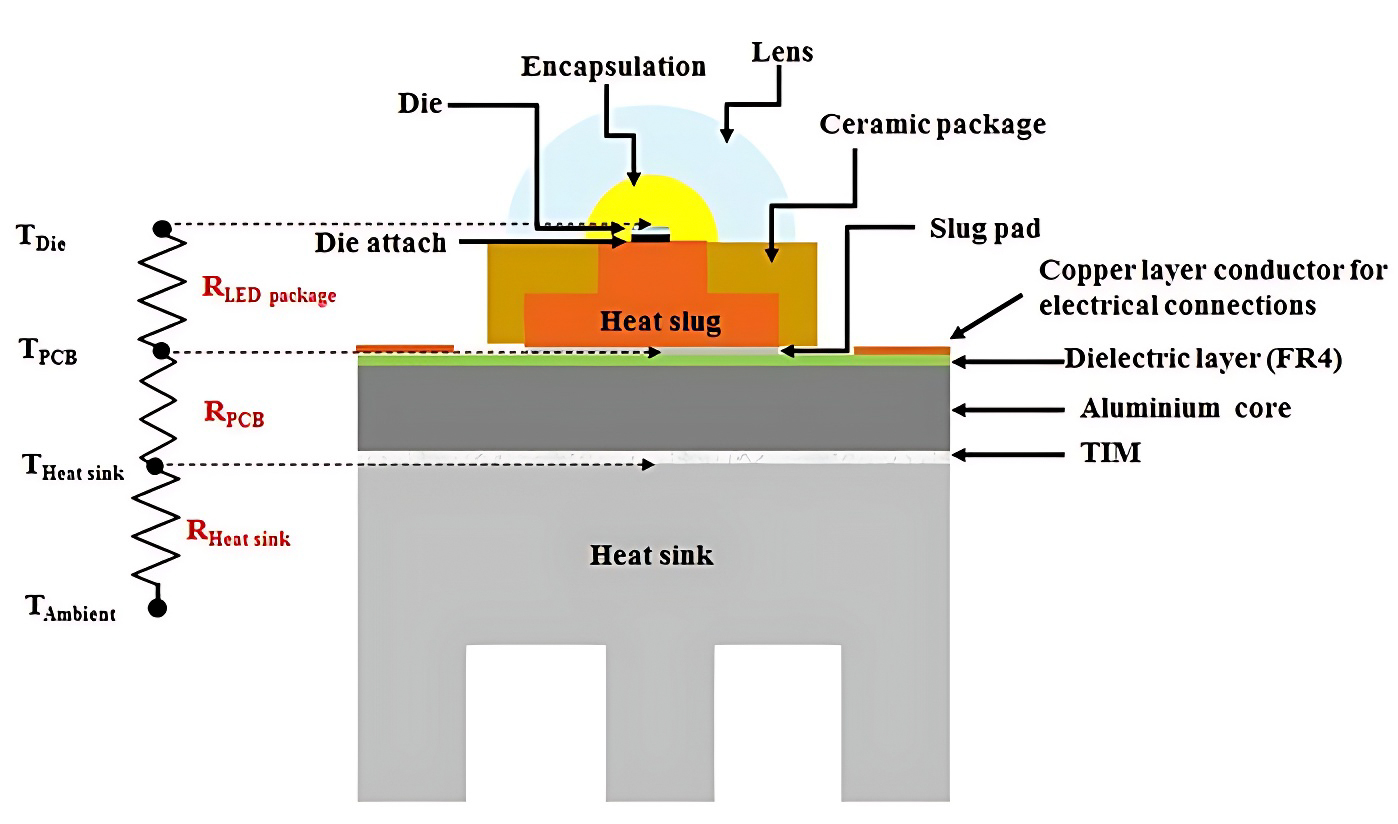
-Material Selection: Aluminum-based PCBs are ideal for high-power LEDs because of their superior thermal conductivity. The aluminum substrate quickly transfers heat away from the LED chip, reducing the working temperature and extending the lifespan of the LED.
-Layout Design: The layout of components on the PCB should be balanced to prevent excessive heat buildup in one area. Adequate spacing between components is necessary to allow air circulation and efficient heat dissipation.
2. Electrical Performance:
LEDs have strict electrical performance requirements. The PCB must provide excellent electrical conductivity and insulation to prevent short circuits or electrical failures.
-Copper Thickness: The thickness of the conductive layer must be optimized to ensure sufficient current-carrying capacity without overloading the system. For high-power LED circuits, thicker copper foil is used to increase current-carrying capacity.
-Impedance Control: In some applications, precise impedance control on the PCB is essential for ensuring signal integrity. Proper impedance matching helps reduce electrical noise and signal distortion, particularly in high-speed or complex LED driving circuits.
3. Reliability and Durability:
LED lighting devices are often used in harsh environments, particularly in outdoor and industrial applications, making the reliability and durability of the PCB essential.
-Moisture Protection: In humid environments, PCBs must be protected against moisture. Common surface treatments include Organic Solderability Preservatives (OSP), hot-air solder leveling (HASL), and gold plating to ensure reliable long-term operation.
-High-Temperature Resistance: For LED devices operating in high-temperature environments, the PCB must be able to withstand elevated temperatures without degradation. Materials such as ceramic PCBs or high-temperature-resistant epoxy resins are often used for these applications.
4. Size and Shape Requirements:
LED devices are often designed to be compact, so the PCB must be flexible enough to accommodate various size and shape constraints.
-Flexible PCBs (FPCs): For portable lighting devices, flexible PCBs are an ideal choice due to their ability to bend and fold. FPCs save space and also enhance the mechanical stability of the device.
PCBs play a vital role in LED lighting systems, as they directly impact the LED's performance and lifespan. By selecting the appropriate PCB type (such as aluminum or ceramic-based boards) and optimizing factors such as heat dissipation, electrical performance, and reliability, the overall quality and longevity of LED lighting devices can be significantly improved. With the ongoing advancement of LED technology, the applications of PCBs in LED lighting will continue to expand and diversify, laying the foundation for more refined and efficient lighting solutions in the future.