Capacitors, as indispensable fundamental components in electronics, play a pivotal role in the design and functionality of printed circuit boards (PCBs). They are not only crucial for the stable operation of electronic systems but also profoundly influence the overall performance and reliability of circuits. Below is a detailed analysis of the six core functions of capacitors in PCBs, expanding on each to provide a more comprehensive understanding of their importance.
1. Filtering
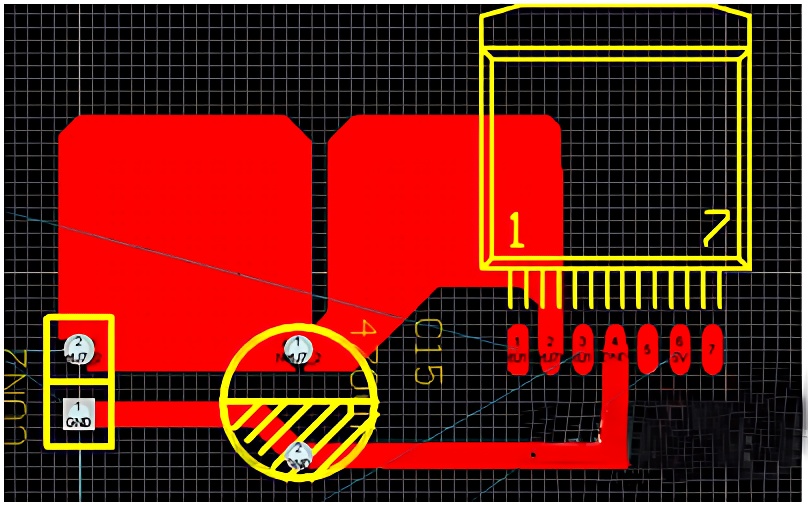
Capacitors serve as vital elements in filtering circuits, effectively removing noise and interference signals from power supplies. They ensure the purity and stability of circuit signals, which is essential for the accurate and reliable operation of electronic devices. In DC power systems, capacitors act as precision "cleaners," filtering out ripple and noise to provide a smooth, stable DC voltage output. This ensures that the power supply remains consistent and does not fluctuate, which can cause errors or malfunctions in electronic circuits. In AC power supplies, capacitors shield high-frequency interference signals, protecting circuits from external disturbances and ensuring accurate and intact signal transmission. This is particularly important in sensitive electronic equipment, such as computers and communication devices, where even small amounts of noise or interference can cause significant problems.
2. Coupling
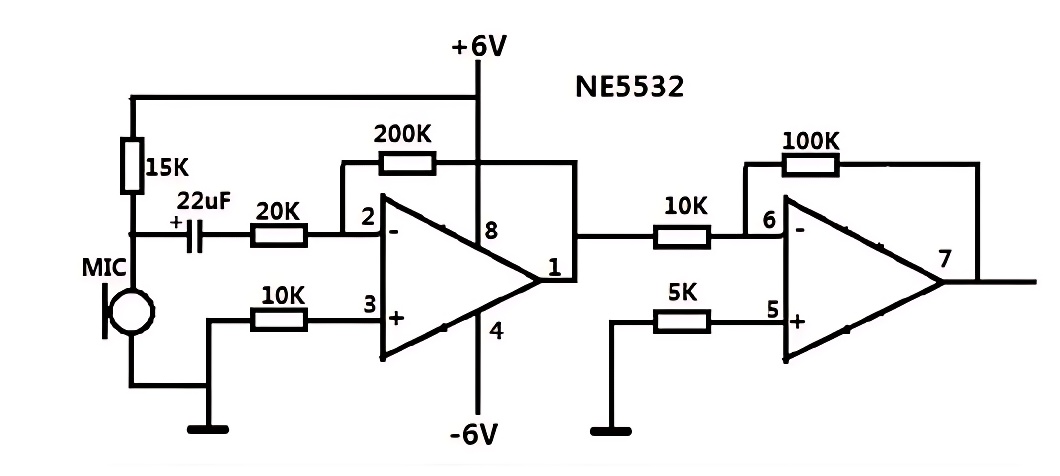
Capacitors function as signal bridges in coupling circuits, transferring AC signals from one circuit to another while isolating DC components. This prevents DC from interfering with AC signals, ensuring that the AC signal remains pure and uncontaminated. In audio amplifier circuits, capacitors serve as "transmitters" for audio signals, seamlessly passing the output signal from the preamplifier to the power amplifier. They maintain DC isolation between the two stages, ensuring stable circuit operation and preventing any potential interference that could degrade the audio quality.
3. Bypassing
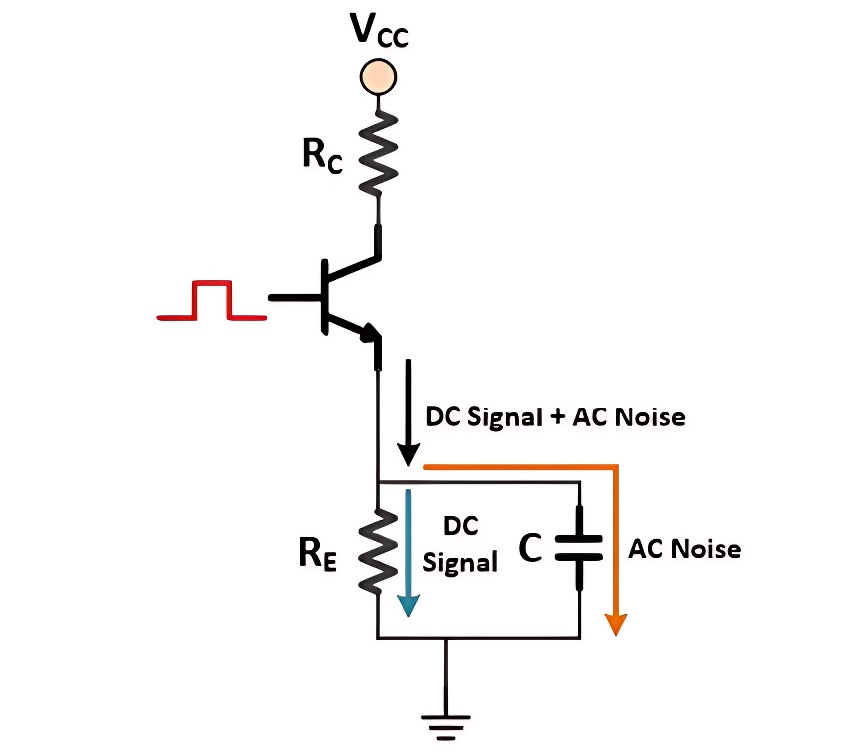
Capacitors in bypassing circuits act as high-frequency signal "diverters," directing high-frequency signals to the ground. This reduces their potential interference with other circuit components, ensuring that the circuit operates smoothly and efficiently. In high-speed digital circuits, capacitors are often used as bypass capacitors for clock signals. They effectively suppress interference from clock signals to other digital signals, enhancing system performance and stability. This is particularly important in high-speed data processing and communication systems, where even small amounts of interference can cause significant delays or errors.
4. Energy Storage
Capacitors exhibit excellent energy storage capabilities, capable of storing large amounts of electrical energy for brief periods and releasing it rapidly when needed. This makes them ideal for use in applications where short bursts of high power are required, such as flashlight circuits and power management systems. In flashlight circuits, capacitors serve as "energy reservoirs," instantly releasing energy upon receiving a trigger signal to produce intense flashes. In power management systems, they act as backup power sources, providing temporary power support during main power interruptions to ensure the continuous operation of critical circuits.
5. Timing
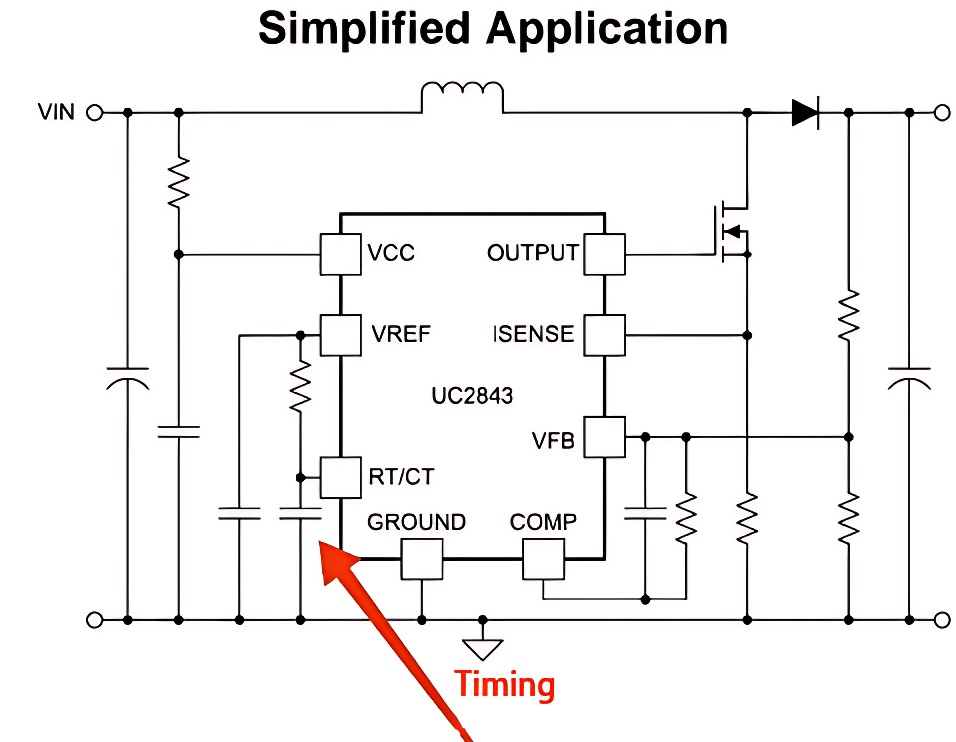
The charging and discharging characteristics of capacitors make them core elements in timing circuits. They allow precise control of circuit time constants, enabling the design of circuits that operate with specific timing requirements. In timer applications, capacitors, along with resistors and other components, enable precise timing control, such as delayed start-up and periodic operations. This is essential in a wide range of electronic devices, from simple timers to complex control systems.
6. Tuning
Capacitors in tuning circuits adjust the resonant frequency of circuits by altering their capacitance. This enables frequency selection and adjustment, allowing electronic devices to receive or transmit specific frequencies. Capacitors serve as tuning elements in radio-receiving equipment, such as radios and televisions. They manually or automatically adjust their capacitance to resonate the circuit at specific broadcast frequencies, thereby receiving clear broadcast signals. This is crucial for the accurate and reliable reception of radio and television signals.
In summary, capacitors play a crucial role in PCBs, serving multiple circuit functions including filtering, coupling, bypassing, energy storage, timing, and tuning. When designing PCBs, selecting appropriate capacitor types and capacities based on specific circuit requirements is essential to ensure circuit performance and reliability. The careful selection and placement of capacitors can significantly improve the overall performance of electronic devices, making them more efficient, reliable, and capable of meeting the demands of modern electronic applications.



